© Benaki Phytopathological Institute
Malhat
et al.
56
al.,
2013; Purnama
et al.,
2015).
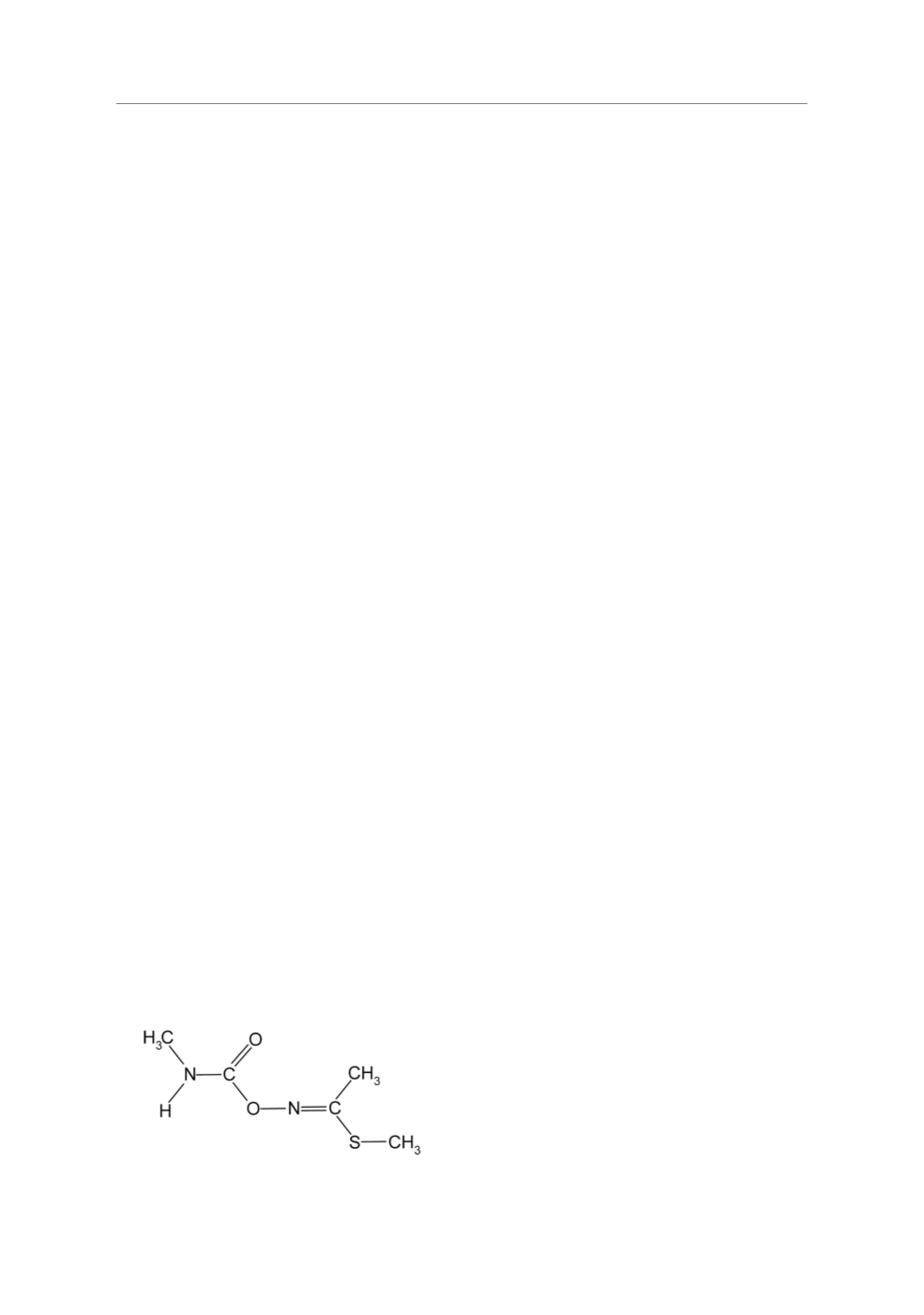
Methomyl (5-methyl-N-(methyl carbam-
oyloxy) thioacetimidate) (Figure 1) has ovici-
dal, larvicidal and adultcidal action against
a variety of insect crop pests as well as
an acaricidal effect (Chakraborty and Pa-
hari, 2002; Furness, 2005). Different extrac-
tion and quantification methods including
HPLC-DAD are used by various scientists for
estimation of methomyl residues in sever-
al vegetables and fruits (Alawi and Rüssel,
1981; Steven and Lin, 1992). The main criteria
for opting any methodology is that analyti-
cal method should be fast, easy, inexpensive
and applicable to different matrices. Cur-
rently, there are no reports in the literature
of the analysis of methomyl in tomato and
soil using the QuEChERS method coupled
with liquid chromatography with a photodi-
ode array detector.
In this study, we set up and validate a
modified QuEChERS method followed by
HPLC-DAD for quantifying methomyl resi-
dues in tomato and soil. Supervised field trials
were conducted to determine the dissipation
kinetics in tomato and soil. From the generat-
ed data, the pre-harvest interval (PHI) was es-
tablished based upon the dissipation pattern
as well as the biological half-life. Further-
more, it is rather imperative to ascertain the
food safety hazard by evaluating residues of
methomyl in terms of their dietary exposure
related to the acceptable daily intake (ADI)
and maximum permissible intake (MPI).
Materials and Methods
Chemical and Reagents
The certified reference standard of
methomyl was provided from central agri-
cultural pesticide laboratory, Egypt, and was
of >99 % purity. All organic solvents were of
HPLC grade and were purchased from Mer-
ck. Primary secondary amine (PSA, 40 μm
Bondesil) and graphite carbon black (GCB)
sorbents were purchased from Supelco (Su-
pelco, Bellefonte, USA). Analytical grade an-
hydrous sodium sulfate was purchased from
El Naser pharmaceutical chemical Co. (Cairo,
Egypt); it was activated by heating at 250ºC
for 4 h in the muffle furnace, cooled and
kept in desiccators before use.
Preparation of standard solution
The stock standard solution (100 mg L
-1
) of
methomyl was prepared inmethanol and sub-
sequently stored at -18°C. An intermediate so-
lution (10 mg L
-1
) was prepared by appropriate
dilution with methanol. The calibration stan-
dards (five calibration points) ranging from
0.005 to 1.0 mg L
-1
(0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1 and
1.0 mg L
-1
) were prepared by successive di-
lution of the intermediate working standard
with pure solvent and matrix extract. All stan-
dard solutions were stored at -18°C in amber
glass bottles until further analysis.
Instrument and apparatus
The food processor was a Thermomix,
Vorwerk. The rotary evaporator was Butch.
The HPLC analysis was performed with an
Agilent 1260 HPLC system, with quaterna-
ry pump, autosampler injector, thermostat
compartment for the column and photo-
diode array detector.
Field experiment
Field experiments were conducted at El-
Hakimayia village, Miet-Gamer Province, El-
Dkahlyia Governorate, Egypt. The field trail
for methomyl was conducted with one com-
mercially available soluble powder formula-
tion (Lannate 90% SP). One treatment was
carried out on 2 August 2011 at the maxi-
mumrecommendeddose (675 g.a.i.ha
-1
). The
treatments, including the untreated control,
were replicated three times in a complete
randomized block design. The average max-
imum and minimum temperature during
the experiment were 25°C and 39°C. There
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of methomyl


