© Benaki Phytopathological Institute
Degradation of methomyl residues in tomato and soil
59
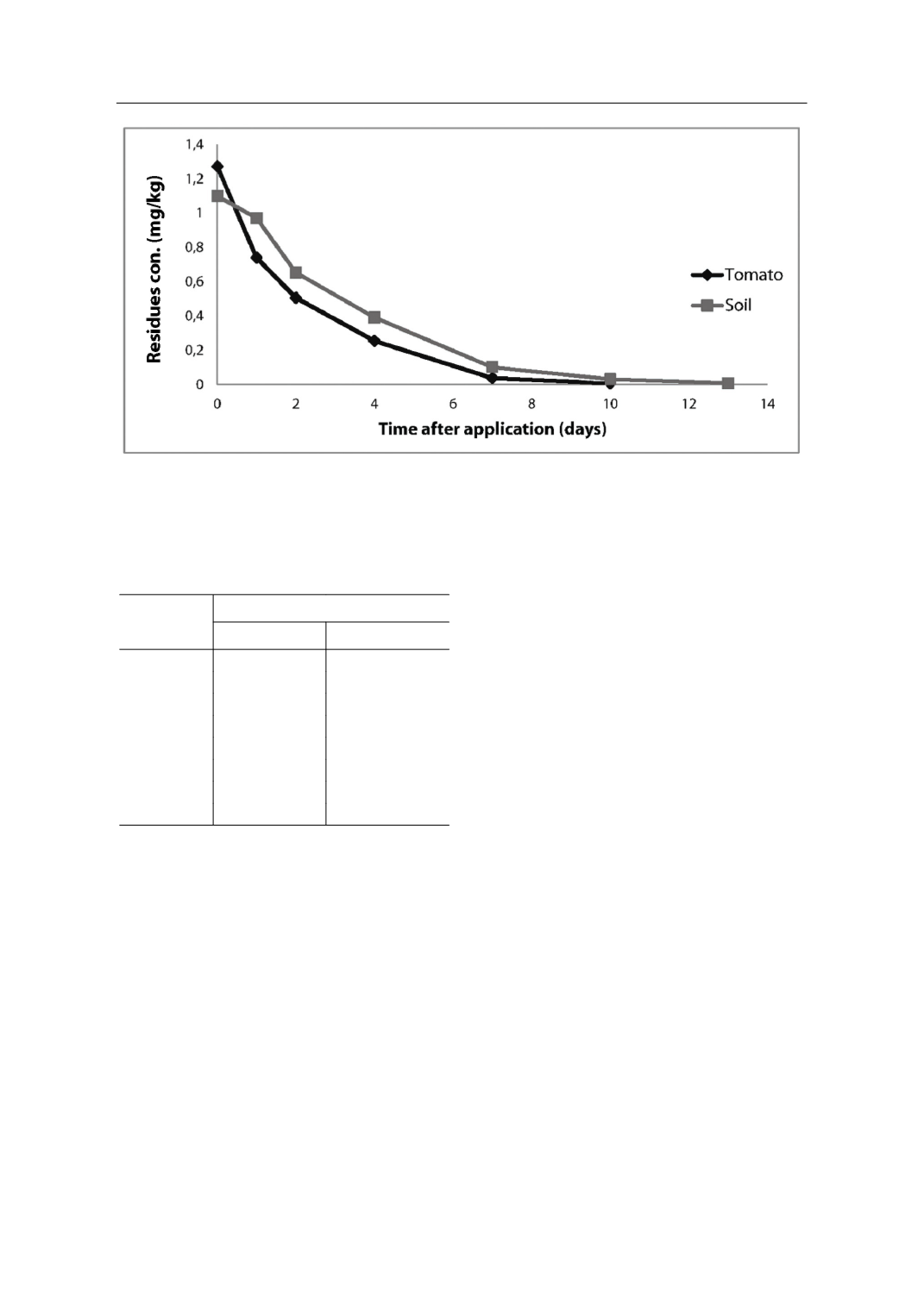
1.8 days. The results showed that the dissi-
pation was also fast in the soil. A decline in
soil residues may be attributed primarily to
growth dilution between application and
sampling, as well as to volatilization which
occurs during the first few days following
application. Other parameters involve sor-
pation-desorpation, chemical and biolog-
ical degradation, uptake by plants, run-off
and leaching (Fang and Qiu 2002; Spunu,
1989; Malhat and Hassan, 2011).
The results showed that the tested pes-
ticides had a higher degradation in tomato
fruits compared with soil, which could be
attributed to the high growth rate of fruits
which causes a dilution of pesticides. In ad-
dition, tomatoes were exposed to various
factors, including direct sunlight and dai-
ly temperature that affected degradation
rates of pesticides.
Risk assessment of methomyl
The risk to the consumer from methom-
yl on tomatoes has been evaluated by com-
paring Theoretical Maximum Residue Con-
tribution (TMRC) of the pesticide with its
Maximum permissible Intake (MPI). The ac-
ceptable daily intake (ADI) for methomyl
has been observed to be 0.02 mg/kg body
weight per day (Tomlin, 2009). The maxi-
mum permissible intake (MPI) was obtained
by multiplying the ADI with the average
body weight of an adult taken as 60 kg (Mal-
hat
et al.
, 2014-a, Loutfy
et al.
, 2015). MPI was
calculated to be 1.2 mg/person/day without
any appreciable life risk. The TMRC has been
calculated by multiplying the maximum
residue levels with average per capita dai-
ly consumption of 77 g of total vegetables
in Egyptian context (WHO, 2003). The TMRC
values on 0 day are found to be 0.098 mg/
person/day (Table 3). As the TMRC for meth-
omyl on tomatoes are found to be less than
the toxicological estimated MPI value of 1.2
mg/person/day, even on 0 day, the consum-
Table 2.
Residue levels (mg/kg ± SD) of
methomyl in tomatoes and soil after appli-
cation.
Time (days)
Residues (mg/kg) ± SD*
Tomatoes
Soil
0
1.272 ± 0.10
1.100 ± 0.30
1
0.740 ± 0.11
0.971 ± 0.10
2
0.506 ± 0.08
0.653 ± 0.09
4
0.254 ± 0.07
0.391 ± 0.05
7
0.038 ± 0.01
0.101 ± 0.03
10
0.007 ± 0.01
0.031 ± 0.01
13
-
0.008 ± 0.005
17
-
-
* Three replicates
Figure 2.
Dissipation pattern of methomyl in tomato and soil at the recommended dosage of application.


